Osteochondrosis of the neck is a degenerative disease in which there is a literal "premature aging", "wear" of the intervertebral discs, joints, vertebrae in the cervical spine.
Some facts about the disease:
- Osteochondrosis of the neck occurs in men and women approximately equally often.
- Most often people aged 30-60 get sick.
- As a rule, the pathology occurs in people who during work must be constantly in one position and perform monotonous movements.
- The cervical spine has some structural features, due to which the disease can have many different manifestations.
What characteristics of the cervical vertebrae cause the symptoms of osteochondrosis?
- There are holes in the lateral processes of the vertebrae - through them the carotid arteries pass through them on the right and left, which supply blood to the brain.
- The initial part of the spinal cord passes through the cervical region - it contains fibers that carry nerve impulses to all parts of the body, provide movement, sensitivity. If there is compression of the spinal cord in the neck, neurological disorders occur throughout the body.
- This part of the spine has great mobility and this predisposes to osteochondrosis (although in most cases the disease still develops in the lumbar spine - not only has high mobility, but also experiences the greatest stress).
- In the neck, nerve roots protrude from the intervertebral foramen, forming the cervical and brachial plexus. They are responsible for movements in the muscles of the neck, arms, shoulder girdle, skin sensitivity and regulation of autonomic functions.
- The first vertebra does not have a massive front part - body - this is a bone ring that is placed on a tooth - a bony growth of the second vertebra. Thanks to this, turning the head to the sides is possible.
Neck pain, headache, weakness, numbness in the hands are symptoms that should force you to visit a neurologist. The examination by a specialist and an examination using modern equipment will help to understand the causes of the pathology and to take the most effective measures.
What happens to the vertebrae in cervical osteochondrosis?
The obscure medical term "degenerative process" refers to the following pathological changes occurring in the cervical spine:
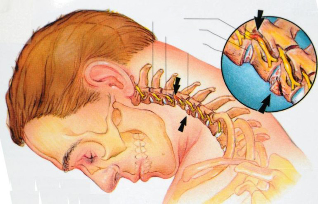
- First, the lesion in osteochondrosis involves the intervertebral discs. They become thinner, thus reducing the distance between adjacent vertebrae. In their outer part small tears, microcracks are formed. Over time, this can lead to a herniated disc.
- Damage to the disc disrupts the stability of the spinal cord.
- They suffer from osteochondrosis of the cervical spine and intervertebral joints - spondyloarthritis develops. It also contributes to the compression of nerve roots.
- The pathological process extends to the vertebrae themselves. Due to the fact that the functions of the intervertebral discs are impaired, the load on them increases. The spine tries to compensate for this disorder, bone growths appear on it - osteophytes.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
During the exacerbation of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, traction is used (the patient is placed on a bed with the headboard raised and the head is fixed with a special loop) to relieve the intervertebral discs. For the same purpose you should wear a Shants collar. Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to relieve pain. In case of severe pain that does not go away in any way, the doctor may block: inject an anesthetic solution into the area of the affected nerve roots. Physiotherapy is used: ultrasound treatment, novocaine electrophoresis.
When the exacerbation subsides, the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine includes massage, physiotherapy, physiotherapy.
One of the main signs of cervical osteochondrosis is neck pain. Many people who face this symptom do not go to the doctor, but prefer to treat "chondrosis" with home methods. There are at least two good reasons to give up self-medication and consult a specialist.
First, painkillers and folk remedies, while helping to relieve pain for a while, do not solve the underlying problem. Pathological changes in the spine continue to increase. Over time, this threatens with more serious consequences. To the point that surgery may be necessary.
Second, neck pain does not only occur in osteochondrosis. There are many other reasons. Only a doctor can understand and prescribe the right treatment.
What symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis should force you to see a doctor?
The main symptom of cervical osteochondrosis is pain. It can appear in different places, depending on the level at which the pathological process is localized: in the neck, in the shoulder girdle, in the arm, in the heart. The pain is dull in nature, can be burning, painful.
Other manifestations of the disease:
- Headache, dizziness, flies in front of the eyes, noise, ringing in the ears.
- Weakness in the muscles of the neck, shoulder girdle, arms.
- Impaired skin sensitivity.
- Shoulder-scapular periarthritis: pain in the neck that extends to the arm, difficulty in abducting the arm above 90 °, weakness and atrophy of the muscles of the shoulder girdle.
- Shoulder-arm syndrome: pain in the shoulder and arm, swelling and stiffness of the fingers, weakness and atrophy of the muscles of the arm.
- Vertebral artery syndrome. Bone growths appear on the vertebrae, which compress the nerves, resulting in a reflex spasm of the spinal artery, which is involved in the blood supply to the brain. The symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are accompanied by constant headaches that start from the nape, spread to the temple, to the crown, nausea, noise in the head, ringing in the ears, flickering bright spots in front of the eyes.
- Anterior rock muscle syndrome. There is the anterior and middle rock muscle on the neck - they are located next to each other, and between them there is a small space in which the nerves and blood vessels pass. In osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebrae, the anterior rock muscle tenses and compresses, leading to symptoms such as pain on the inner surface of the forearm, shoulder and fingers. Sometimes the pain radiates to the back of the head. The skin on the hand may become cold, pale, and tingling may occur.
- Epicondylitis syndrome. In the lower part of the shoulder, on the side of the elbow joint, there are bony protrusions - epicondyle. With epicondylitis syndrome caused by cervical osteochondrosis, they experience painful sensations that increase when pressed. There are other symptoms: neck pain, pain when pressing certain points in the cervical spine.
If two parts of the spine are affected at once, with cervicothoracic osteochondrosis, symptoms may include pain between the shoulder blades in the area of the heart.
Osteochondrosis increases the risk of intervertebral hernia and stroke. If you have any of the above symptoms, talk to your doctor.
It is better not to self-medicate. Even if you have proven methods that can usually help you manage your pain, that doesn't mean you're doing it right.
Pain can be caused not only by osteochondrosis, but also by intervertebral hernia, muscle disorders (myofascial pain syndrome) and be a symptom of other diseases. To properly treat the disease, you need to understand the causes of it, to make a differential diagnosis. This is only possible in a clinic.
To determine the cause of the disease and properly treat the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis, you need to visit a neurologist, to undergo an examination.
At the heart of cervical osteochondrosis is the defeat of the intervertebral discs. Their chemical composition is disturbed, at first they swell, then decrease in size, cracks and tears appear in their outer part, they become denser. Then the degenerative process spreads to the vertebrae, intervertebral joints. Due to the reduction of the height of the intervertebral disc, the load on the vertebrae increases, bone growths appear on them - osteophytes.
What are the causes of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine?
There is no consensus on the causes of cervical osteochondrosis. It is believed that different conditions cause diseases, there are different points of view:
- Age-related changes in the spine. However, almost all people over the age of 40 have skeletal changes, but not everyone has osteochondrosis.
- Neck injuries. Often among the causes of the disease are trauma: bruising of the neck, compression fracture, spinal subluxation. Chronic injuries, such as during intense training for athletes, constant awkward bending postures, and recurrent whip injuries in motorists, may be relevant.
- Congenital anomalies of the vertebrae: cervical ribs, fusion of adjacent vertebrae, fusion of the first vertebra with the occipital bone, etc.
- Profession. More often the disease affects people who work in a monotonous position, constantly making the same type of movement.
- Blood supply to the spine, venous insufficiency, edema of the nerve roots.
- Autoimmune Disorders.Conditions in which the immune system does not work properly, attacking its own connective tissue, ligaments of the body.
See a neurologist. An experienced medical professional will understand the source of your health problems and prescribe the right treatment.
Causes of exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis occurs in the form of alternating exacerbations and periods of improvement when symptoms cease to bother for some time. Another exacerbation can be caused by the following reasons:
- Uncomfortable, sudden movements of the neck.
- Long stay in a uniform awkward position. For example, a neck may start to hurt after prolonged use of the computer after sleeping on an uncomfortable pillow.
- Stress, nervous tension. With chronic stress, spasms appear in the muscles of the neck, this can lead to another exacerbation.
- Various diseases, exacerbations of chronic diseases.
- Hypothermia. For this reason, exacerbations in many people occur in the fall.
- Improper, illiterate self-medication. For example, massage and therapeutic exercises are useful during remission, but contraindicated during exacerbations.
Which diseases can have similar manifestations?
Very often the manifestations of "osteochondrosis" are actually associated with a completely different disease. For example, the cause may lie in the muscles - there is such a condition as myofascial pain syndrome. The pain arises from the constant tension of the same muscles.
Sometimes "cervical osteochondrosis" is considered dizziness associated with otolithiasis, a condition in which calcium salt crystals accumulate in the inner ear.
Pain and crunch in the neck, headache - when these symptoms appear, many people "diagnose" osteochondrosis. Everything is clear - when it hurts, you need to take painkillers or make a prick, apply heat and everything will pass. Why go to the doctor when you can handle it yourself?
Often, however, self-medication does not lead to anything good. Painful attacks may become more frequent, severe and prolonged over time. If you take painkillers uncontrollably almost every day, you can get stomach or kidney problems. After all, any drug has side effects.
And the cause of pain is not always the main cause of osteochondrosis. To find out the real cause and find out how to deal with it effectively, you need to see a doctor and get examined.
How does a neurologist diagnose cervical osteochondrosis? What happens in the doctor's office during the examination?
During your first visit, the neurologist will ask you a few questions:
- How long have you had headaches, neck pains?
- Where does the pain appear? What kind of character are they: stabbing, pain, shooting, pulling?
- When does pain usually occur? What provoked him? After what do you feel better?
- Have you ever been a doctor? Have you been examined and treated? Which one? How long ago?
- What other symptoms bother you?
- What other chronic diseases do you have?
- Have you had a recent neck injury?
The doctor will then do a neurological examination, checking your reflexes, skin sensitivity, muscle strength and tone. You will be asked to turn, tilt your head to the side, forward, backward. The doctor will press lightly on your head, on certain points on your neck, to determine the onset of pain.
After the examination, you will be diagnosed and prescribed the necessary diagnostic methods.
What diagnostic methods are used in osteochondrosis of the cervical spine?
The cervical osteochondrosis test usually includes the following diagnostic methods:
- Radiography of the cervical spine.
- According to the indications, X-ray contrast examinations are prescribed: myelography (introduction of contrast in the space around the spinal cord), discography (introduction of contrast in the intervertebral disc), angiography (introduction of contrast in the vessels).
- Computed tomography.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- In severe neurological disorders, you may be prescribed electroneuromyography, a test that determines the passage of electrical impulses to nerves and muscles.
Cervical osteochondrosis often resembles angina pectoris. If after the examination the doctor still has doubts about the diagnosis, you will be prescribed an ECG and other diagnostic methods.



































